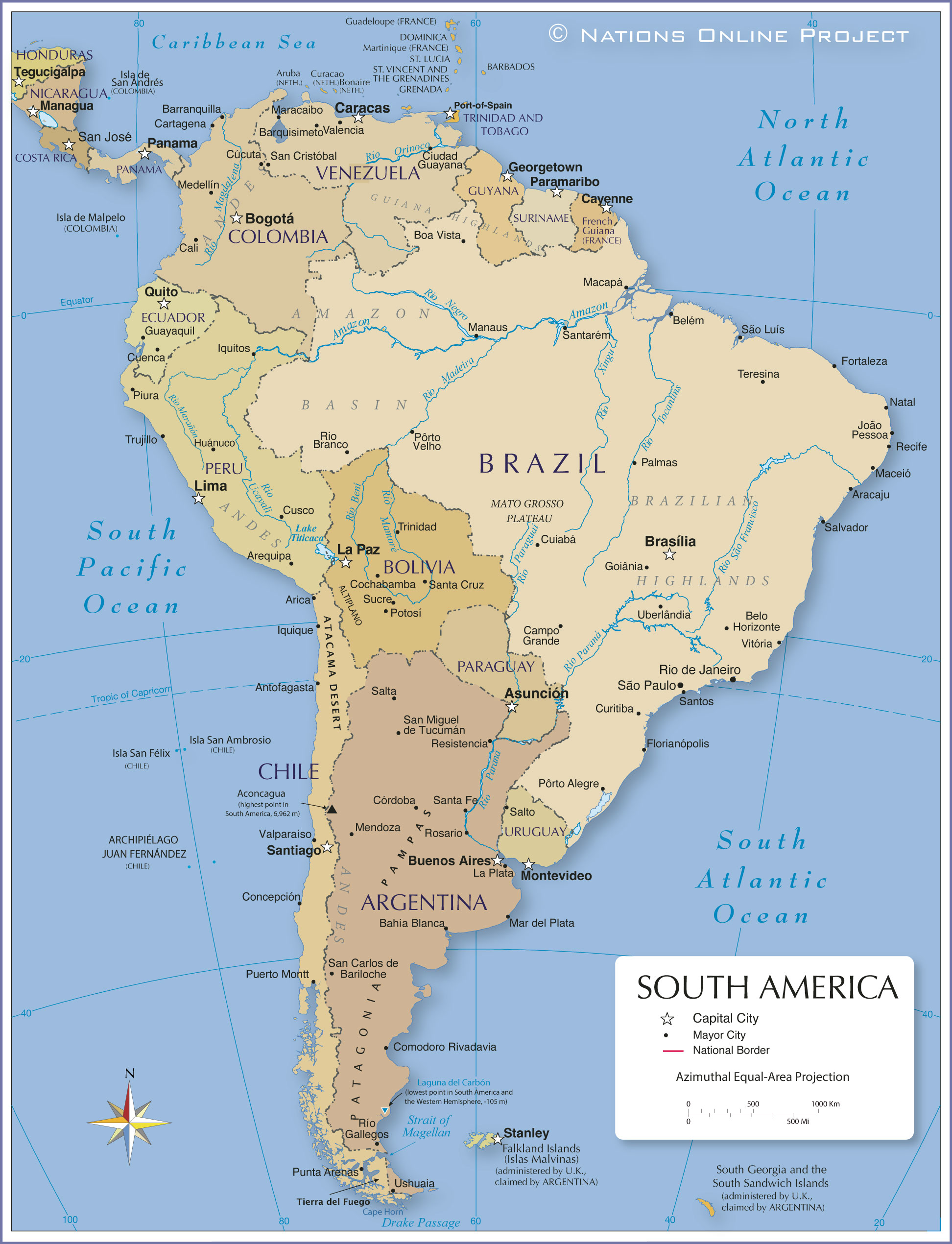
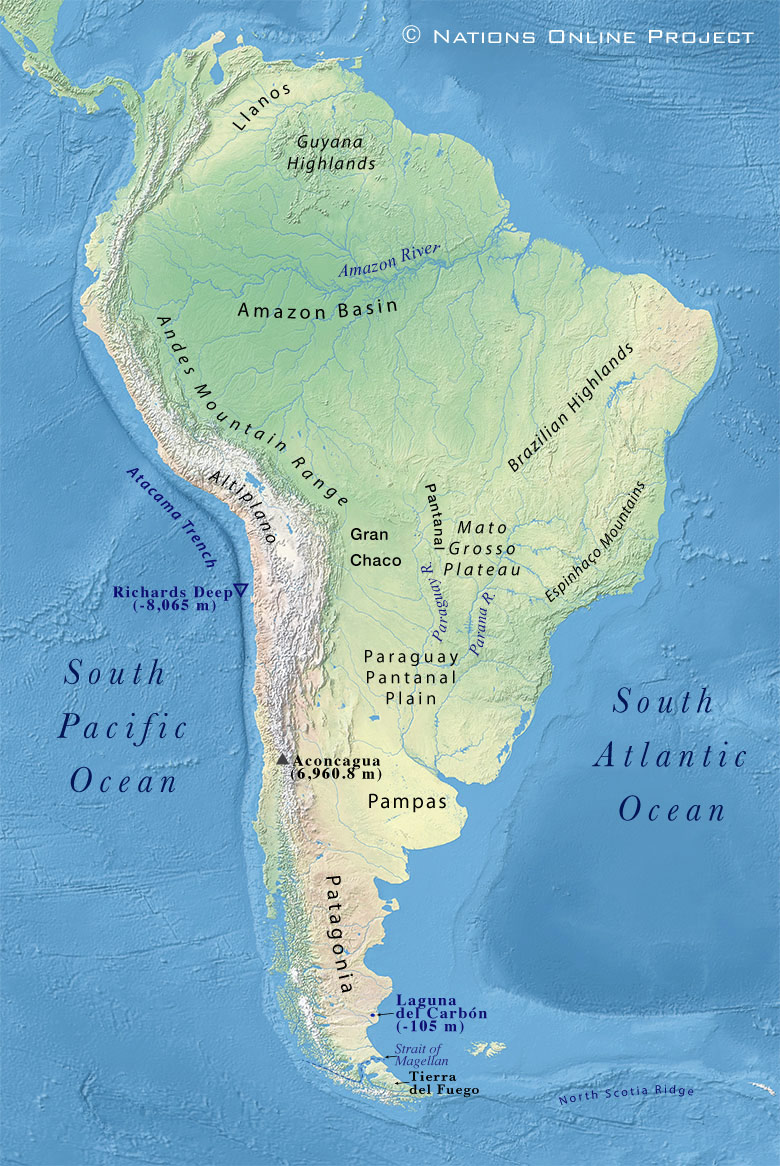
Major geographical features of South America
List of the main physical regions of the South American continent.
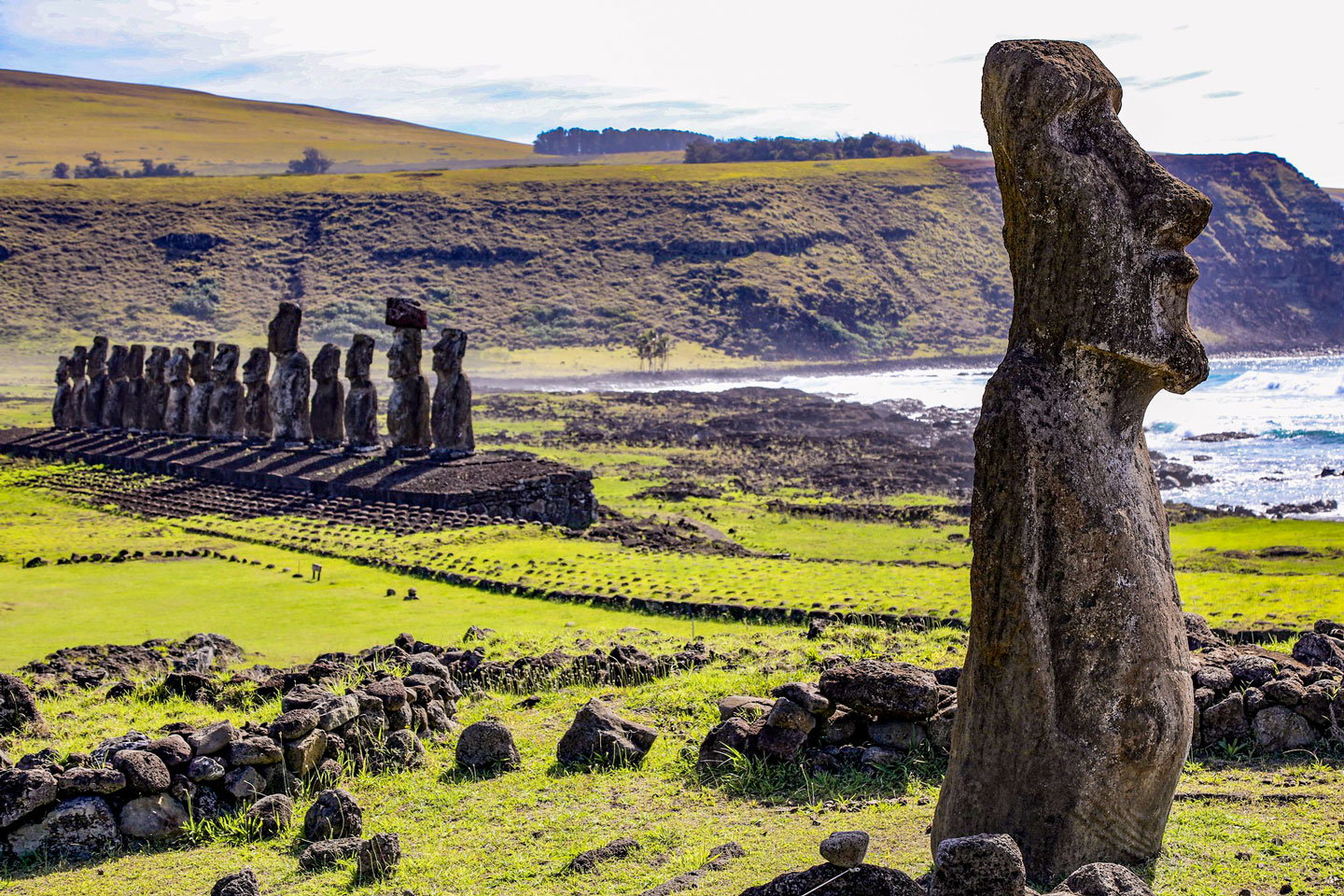 The Moai figures on the Easter Island (Rapa Nui) are monolithic human figures made by the Rapa Nui people between the mid-13th and 16th centuries.
Image: Wendi Halet
The Moai figures on the Easter Island (Rapa Nui) are monolithic human figures made by the Rapa Nui people between the mid-13th and 16th centuries.
Image: Wendi Halet
The continent includes the
Falkland Islands, an archipelago of more than 100 islands in the South Atlantic Ocean, an overseas territory of the UK since January 1833, claimed by Argentina.
Easter Island (Isla de Pascua; Rapa Nui) is the easternmost island of Polynesia in the southeastern Pacific Ocean. The Chilean dependency lies more than 3,700 km (2,300 mi) west of the coast of Chile.
The island is famous for its nearly 900 monumental statues, the
Moai, created by the islanders between the 13th and 16th centuries.
The
Galápagos Islands are an archipelago in the Pacific Ocean on the equator, about 1,000 km (620 miles) west of Ecuador's coast. The Galapagos Islands are known for their large number of endemic species, which Charles Darwin studied in the 19th century. He published the results of his studies in his famous book "The Origin of Species." Today, the
Galápagos Islands are a World Heritage Site.
Tierra del Fuego
The archipelago of Tierra del Fuego forms the southern tip of the South American continent.
Isla Grande de Tierra del Fuego, the largest island in South America, is separated from the mainland by the Strait of Magellan.
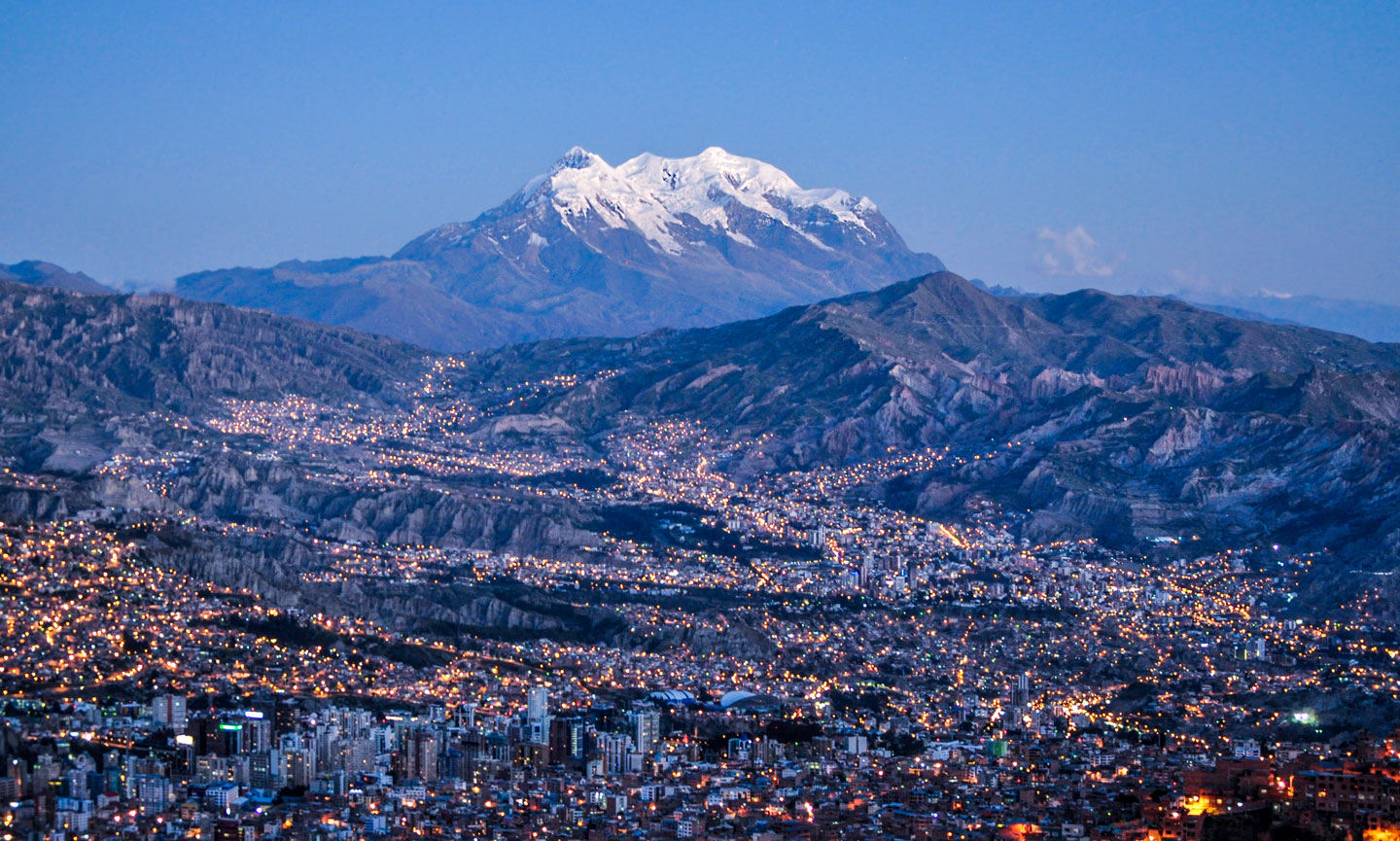 View of La Paz. Bolivia's third largest city and the seat of the country's government is located on the Altiplano. La Paz is the highest capital city in the world at 3,640 m. In the background, the 6,438 m (21,122 ft) high snow-covered Illimani Mountain, the highest mountain in the Cordillera Real, a subrange of the Andes.
Image: EEJCC
View of La Paz. Bolivia's third largest city and the seat of the country's government is located on the Altiplano. La Paz is the highest capital city in the world at 3,640 m. In the background, the 6,438 m (21,122 ft) high snow-covered Illimani Mountain, the highest mountain in the Cordillera Real, a subrange of the Andes.
Image: EEJCC
The highest point in South America is
Mount Aconcagua (6,962 m; 22,840 ft), located in the
Andes Mountain Range in Argentina.
The
Andes are a continental mountain range in western South America, the
longest mountain range in the world. The various Cordilleras of the Andes stretch for more than 8,600 km along the continent's west coast, crossing seven countries.
The Andes were formed by plate tectonics, the collision of two crustal plates. The denser oceanic Nazca plate had pushed under the lighter continental South American plate and formed a subduction zone. In the process, the Nazca plate is pushed downward, creating a trench, and the continental crust of South America is pushed upward, creating the Andes mountain range.
The subduction zone is an area of intense volcanic activity; it forms the eastern section of the
Pacific Ring of Fire. The subduction zone of South America is one of the world's most earthquake-prone regions.
[USGS]
Altiplano
The Altiplano (High Plateau) is a high-altitude tableland in the Andes mountain range shared mainly between Peru and Bolivia, with some areas in Chile. The plateau lies at an average altitude of about 3,750 m (12,300 feet), grasses and shrubs dominate the landscape. The Altiplano is the site of
Lake Titicaca and the
Salar de Uyuni (see below). The Altiplano is also Bolivia's most densely populated region.
La Paz, Bolivia's second-largest city and administrative capital, is located on the Altiplano.
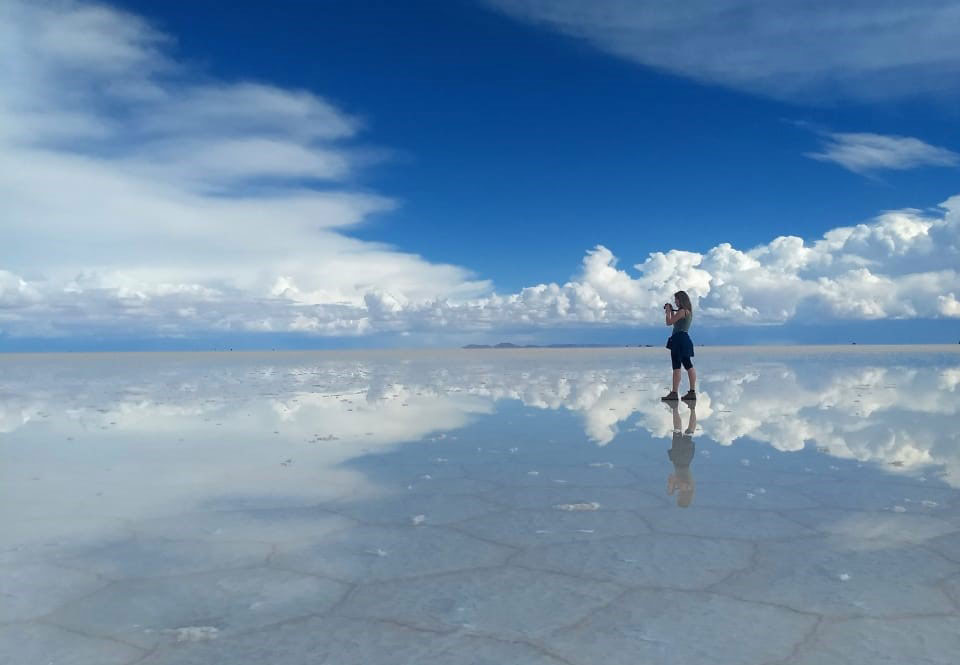 Reflection of the sky in the Salar de Uyuni.
Reflection of the sky in the Salar de Uyuni. The world's largest salt flat is located in the southwest of Bolivia at an elevation of 3,656 m (11,995 ft).
[NG]
Image: Jeferson Herbert
The Gran Chaco (Quechua: Hunting Land) in the interior of the South American continent is a rather sparsely populated subtropical semiarid alluvial lowland in western Paraguay and northern Argentina.
Llanos
The Llanos (Spanish: "Plains") are a vast tropical grassy plain east of the Andes Mountains in Colombia and Venezuela in northwestern South America.
Pampas
The Pampas (Quechua: flat surface area) is a vast area of nearly treeless and fertile grasslands in southeastern South America.
Pantanal
The Pantanal is an extensive tropical seasonal wetland and savanna ecoregion at the headwaters of the
Paraguay River in southwestern Brazil; it is the world's largest tropical wetland area.
Patagonia
Patagonia is a plateau in the southern part of South America; it covers a vast area from the Colorado River in central Argentina to the Strait of Magellan and from the eastern foothills of the Andes to the Atlantic coast.
Rivers
Major rivers are the Amazon River (Amazonas) with its tributaries Rio Madeira, Rio Negro, and Rio Xingu, Rio Magdalena, Rio Orinoco. The
Amazon River is the
largest river by discharge of water in the world.
The Tocantins River, São Francisco River, and Rio Paraná are not tributaries of the Amazon.
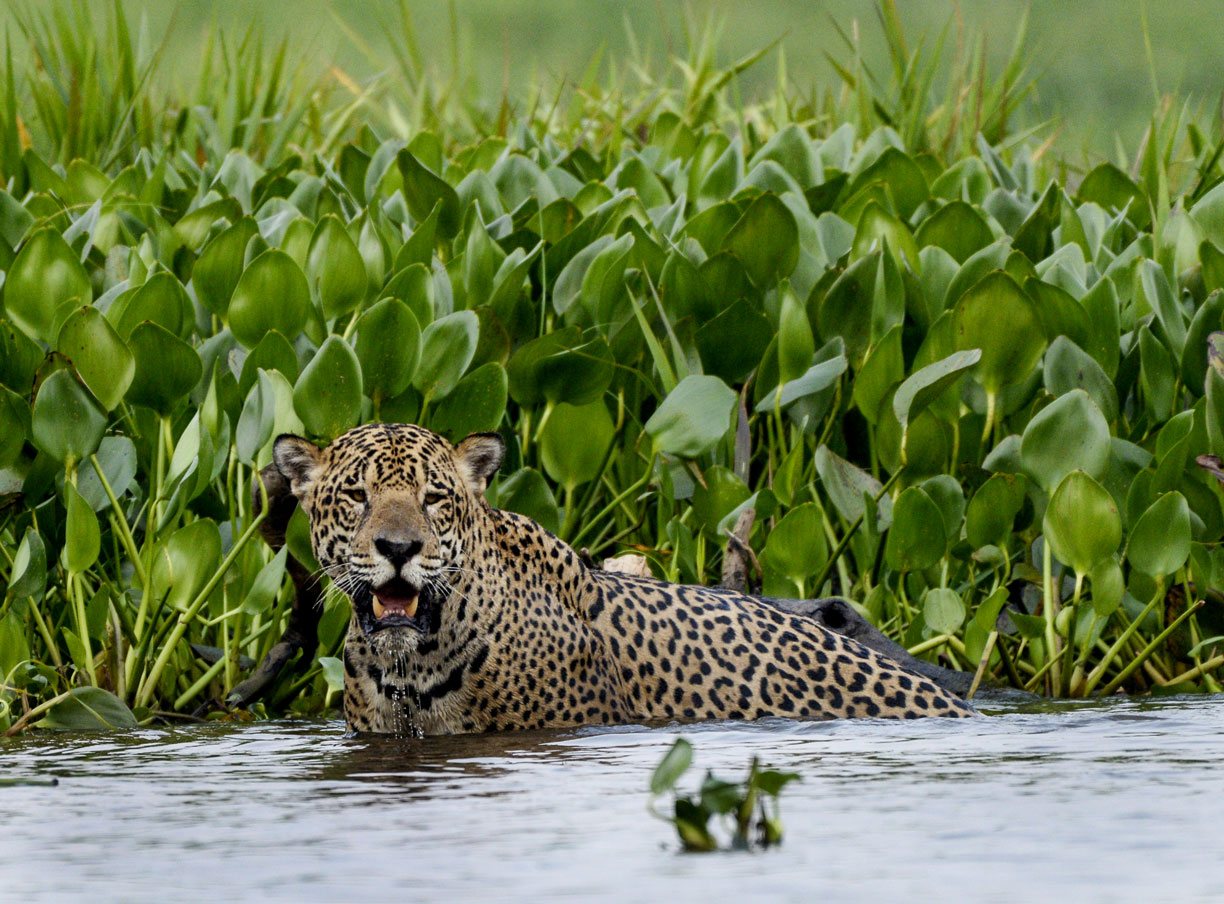 A jaguar in the northern Pantanal, the largest tropical wetland in the world, located mainly in the Brazilian state of Mato Grosso do Sul. Jaguars used to be found from the southwestern United States across South America to almost the far north of Argentina. Now they are virtually extinct in half of their historic range. [WWF]
Image: Jan Fleschmann
A jaguar in the northern Pantanal, the largest tropical wetland in the world, located mainly in the Brazilian state of Mato Grosso do Sul. Jaguars used to be found from the southwestern United States across South America to almost the far north of Argentina. Now they are virtually extinct in half of their historic range. [WWF]
Image: Jan Fleschmann
in western Venezuela is an inlet of the Caribbean Sea and the largest lake in South America.
Lake Titicaca in the Andes, on the border of Peru and Bolivia, is the continent's largest lake; it is also the highest navigable lake in the world at an altitude of 3,812 m (12,507 ft).
South America Geographic Extremes
Geographical highlights of South America: highest point, deepest point, longest mountain range, etc.
The
highest point in South America is
Aconcagua at 6,960.8 meters; it is the highest mountain in the Americas and the highest peak outside of Asia.
The
lowest point of South America, at -105 m, is
Laguna del Carbón, a salt lake in Santa Cruz province of Argentina.
The
Amazon River is the largest river by water discharge and the second-longest river system in the world after the Nile.
Lake Titicaca, on the border of Peru and Bolivia, is the continent's largest lake; it is also the highest navigable lake in the world at 3,812 m (12,507 ft).
The extreme points of the South American mainland.
The
northernmost point is at
Punta Gallinas, a cape at the tip of the Guajira Peninsula in northern Colombia.
The
southernmost point of the mainland is at
Cape Froward on the southern tip of the
Brunswick Peninsula at the northern shores of the Magellan Strait in Chile. The southernmost point of the continent is at treacherous
Cape Horn.
The
westernmost point is at
Punta Pariña, a cape in Piura Region in northwestern Peru.
The
easternmost point is at
Ponta do Seixas, also known as Cape Branco in Brazil's Paraíba state near its provincial capital
João Pessoa.


_Carbajal_Valley.jpg)